Sequential
Last updated: Dec. 11, 2025Definition
One is claimed to have happened earlier and the other later with respect to each other
English examples
- He cut the grass and then he slept.
- He ate and afterwards he slept.
Kovol examples
Type 1
- oboob, yab, mohis ab ogo wogonoongg amemind.
"they got it, (then) went, (and then) spoke with the people of the place" - Mandeb tolo Womune isombo libemind.
"They wandered around (and then) in the Womune jungle upstream they came up"
Type 2
- pige. Om watotogom
"she put (it), (then) I weaved (it) together here."
Type 3
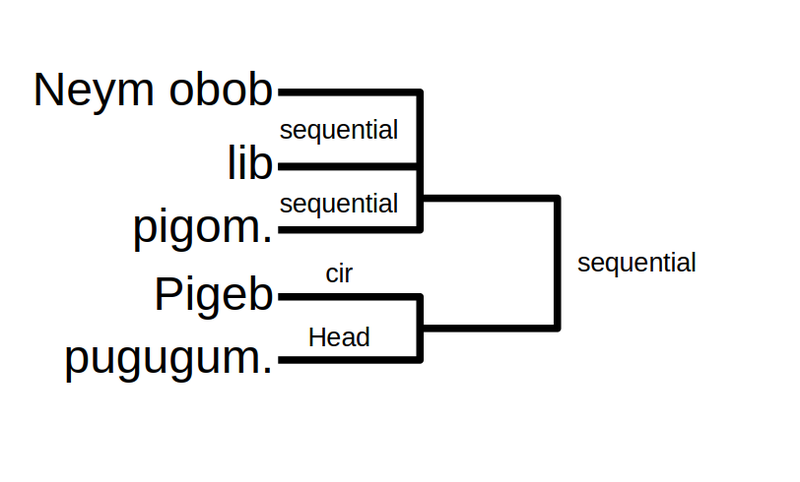
- Neym obob lib pigom. Pigeb pugugum.
"I got the tree, (then) came up (and then) put it. (Having) put I (then) sat."
Kovol description
There are 3 ways to show sequential propositions in Kovol.
Type 1 uses medial verb suffixes to create a verb chain. Each dependent clause in the chain is an event in the sequence. This is used to create "complex events" consisting of several verbs. Complex events are things like "getting and coming", "coming and speaking" or "cutting and breaking and putting". These verbs belong together as a single complex action.
Type 2 uses two independent clauses simply next to each other. The juxtaposition implies a sequential relationship. The use of juxtaposed independent clauses may also be Equivalence
Type 3 is used to sequentially link verb chains. In the example, the getting and putting of the tree is one complex event which is followed by sitting as a different event. A Circumstance-head relationship is used. The recapitulation of the last verb in the previous chain as a medial verb is followed by the next event. It can be illustrated as below:
Degree of confidence
High